BLOG | ITSM
Process Automation as a Growth Driver
Transforming manual processes into efficient workflows in IT service management.
BLOG | ITSM
Transforming manual processes into efficient workflows in IT service management.
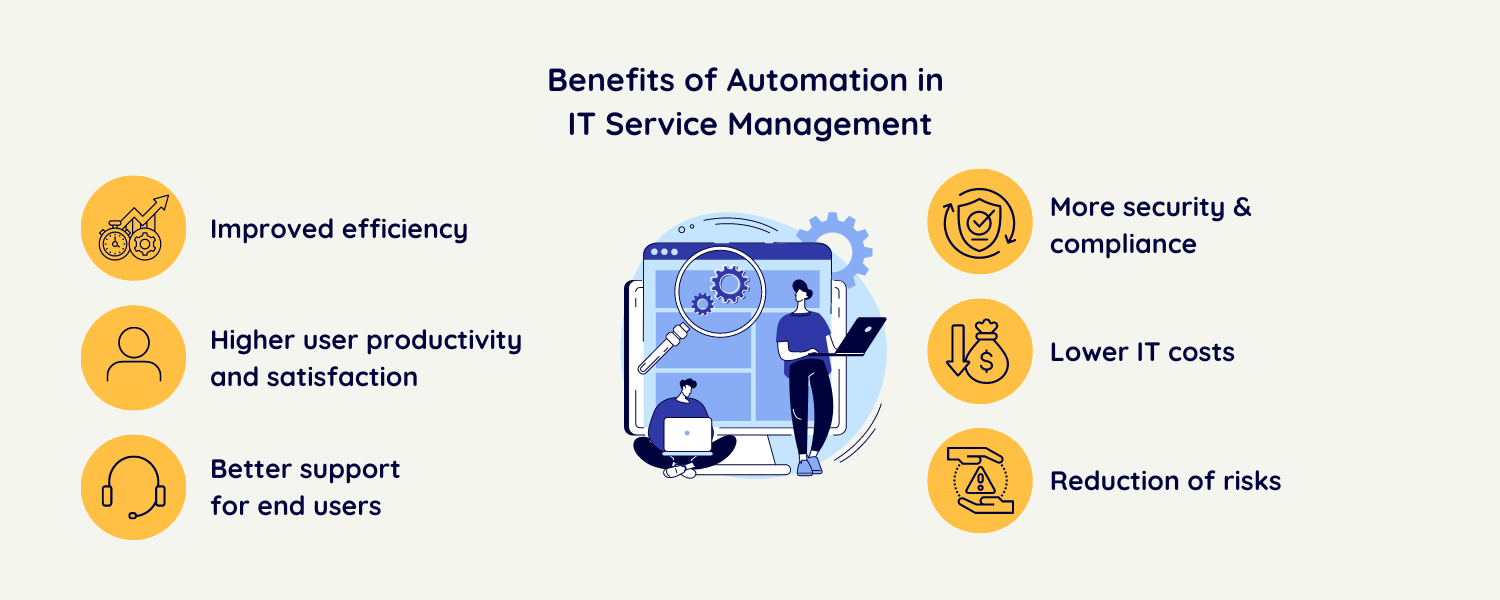
Process automation in IT service management (ITSM) is a key growth driver for businesses, as it leads to improvements in efficiency, productivity, and quality of services. By automating processes, companies can better utilize their resources, reduce errors, and shorten response times to customer requests.
This blog article highlights the diverse benefits of automation in ITSM for IT organizations of varying maturity levels and shows how they can sustainably improve the efficiency and quality of their IT services.
Automation in IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the use of technologies to optimize and streamline repetitive and manual IT processes. This can include simple tasks, such as automatically creating incident tickets, automating workflows, and complex systems that leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to enable proactive and self-healing IT services.
Efficiency Increase
Process automation eliminates manual, error-prone processes and accelerates the handling of service requests and incidents. Companies can better utilize their resources and reduce time-consuming tasks, increasing productivity.
Cost Reduction
The automation of routine tasks contributes to cost savings, as you need to spend less time and resources on manual activities. Especially open source solutions offer mid-sized companies multiple opportunities to save IT budget and reduce overall costs. Firstly, the otherwise hefty license fees are eliminated. Furthermore, open source solutions like OTOBO offer cost-effective options for process automation and flexible adaptation of software to individual business requirements
Process Optimization
Process automation helps standardize and optimize existing ITSM processes. IT Service Management solutions assist IT organizations in structuring their IT services and processes consistently and transparently through a service catalog, making them available to employees via a user-friendly self-service portal, and thereby increasing employee satisfaction.
Resource Efficiency
Through process automation, you unburden your team and gain valuable time for tasks and initiatives with higher added value. The prioritization and automatic assignment of tasks ensure that you utilize existing resources efficiently and tackle the most important tasks first.
Integration of Advanced Technologies
Highly developed IT organizations integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into their automation solutions. These technologies enable proactive error identification, predictive maintenance, and faster resolution of disruptions. The overall performance and reliability of IT services are further improved.
Implementing an automation solution, unless it’s already a modular component of the ITSM solution, can be technologically demanding, especially when integrating existing legacy systems and processes. It requires careful planning and may necessitate significant investments in new technologies.
Naturally, open source solutions offer flexible and cost-effective solutions for automating workflows and integrating third-party solutions based on open REST/SOAP interfaces.
Those who want to completely avoid the investment for operating the IT infrastructure can circumvent this technological and economic barrier by opting for an ITSM solution in a managed services provider model.
Despite the relieving effect of process automation, the abrupt transition from manual to automated processes can evoke resistance among employees. After all, they have often adapted to the current environment and its challenges over many years and built up corresponding solution knowledge.
It is therefore crucial to ensure effective change management and training programs to promote acceptance and trust in the new systems and processes.
Automation introduces new security challenges. Automated systems must be carefully monitored to ensure that data integrity and security are maintained throughout the entire automation process.
For incident management, it is crucial that both master and infrastructure data, as well as the data captured for the process, are complete, correct, and up-to-date. Automated systems should be able to recognize inconsistencies or missing information and take measures to improve data quality. For example, OTOBO can automatically check if all required fields in an incident capture mask are filled out and prompt the creator to make corrections.
Even in the automation of change management, all data on changes made to the IT infrastructure must be stored correctly and revision-securely. This includes, for better traceability, not only the historization of changes but also the documentation of requests and approval steps.
In the discipline of problem management, only authorized persons should have access to certain data. Role-based access control helps ensure that only authorized users can make changes or access confidential information (e.g., the details of a sensitive problem analysis).
For service level management, it is essential to archive historical data on service performance and availability in order to analyze long-term trends and plan future improvements. Automated processes should also ensure that data is archived in accordance with company policies and retained for the required duration.
Many ITSM processes require the exchange of data between different systems and tools. For example, in asset management, there must be at least an automatic integration between the Configuration Management Database (CMDB), incident and change management, so that all information about IT assets and their states is consistent and up-to-date.
Finally, when automating ITSM processes, legal requirements and compliance regulations must also be taken into account. Automated processes, such as those used for employee onboarding and offboarding, must ensure that personal data is used only for the intended purpose in accordance with the EU GDPR (European Union General Data Protection Regulation) and that individuals can exercise their rights, such as the right to information or erasure of stored data.
Process automation in IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the use of technology to perform repetitive tasks without human intervention. It improves the efficiency and consistency of IT processes and enables IT teams to focus on initiatives that offer higher value.
The successful implementation of process automation requires careful planning and a clear strategy. It is essential to consider the specific needs and maturity level of the IT organization to achieve the best possible results.
Goal Definition and Needs Analysis
For IT organizations with a low maturity level, it is crucial to define clear goals for automation. Start by conducting a needs analysis to determine which processes would benefit most from automation.
Service Request Management
Automating Service Request Management is an important first step. By automating request processing and approval workflows, response times can be significantly reduced, and requester satisfaction increased. In particular, a user-friendly self-service portal can already provide significant relief for IT in an early phase.
Incident Management
Another sensible automation field is incident management. By automating categorization, prioritization, routing, and service quality monitoring, IT teams can respond faster to outages and minimize service downtime.
Change Management
A simple change process at the beginning of the maturity curve ensures that changes to IT systems and processes are carried out in a planned and controlled manner, reducing the risk of errors. It is one of the ITSM processes that should be standardized and automated early on in an organization’s IT maturity journey to achieve further efficiency gains.
Selecting the Right Tools
Choosing the right automation tools is another crucial step. Open source solutions like OTOBO offer cost-effective and flexible options that can be tailored to the specific needs of smaller IT organizations. These tools enable the automation of basic processes without requiring significant additional investments.
Phased Implementation
Start by automating simple, repetitive tasks (e.g., service request and incident management) and build upon these successes (e.g., fundamental change management and service level management). This approach minimizes risks and allows the team to become familiar with the new processes.
Integration and Adaptation
For IT organizations with a medium IT maturity level, integrating process automation into existing systems and processes is crucial. Automation solutions should offer comprehensive adaptation capabilities to seamlessly integrate into the existing IT infrastructure. Typical next ITSM disciplines to be pulled into process automation are comprehensive change management, problem management, and configuration management (CMDB).
Change Management
By automating even complex changes, organizations with a medium IT maturity level can achieve significant benefits. The automated processing of change requests, risk and impact analyses, as well as the approval of complex changes saves valuable time, minimizes risks, and relieves both resources and the IT budget.
Problem Management
The task of problem management is to identify recurring incidents, analyze their causes, and eliminate them to prevent the recurrence of the incident. Negative impacts on ongoing operations are avoided, the number of incidents reduced, the team further relieved, and service quality improved.
Training and Support
Ensure that IT personnel receive comprehensive training to effectively utilize the newly automated processes. Offer continuous support and training to foster acceptance and trust in automation.
Monitoring and Optimization
After implementation, it is essential to continuously monitor and optimize the automated processes. Use user feedback and performance data to further improve automation and adapt to new requirements.
Advanced Automation and Integration
Highly developed IT organizations can benefit from advanced automation technologies that integrate AI and machine learning. These organizations should focus on proactive monitoring, self-healing systems, and the automation of complex service processes.
Proactive Monitoring and Incident Resolution
Advanced automation solutions that integrate proactive monitoring and self-healing mechanisms leverage AI and machine learning to predict incidents and automatically resolve them.
Service Level Management
Through the automation of Service Level Management in conjunction with the service catalog, it is ensured that SLAs (Service Level Agreements) are continuously monitored and fulfilled. Automated reporting and escalation processes help to guarantee the adherence to service commitments while increasing transparency and traceability.
Strategic Planning and Continuous Improvement
The implementation of process automation in highly developed IT organizations requires strategic planning that takes into account long-term goals and continuous improvements. Create a roadmap for automation, which is regularly reviewed and updated to ensure that automation aligns with business requirements.
Ensuring Compliance and Security
Automated systems must be regularly checked for compliance with security and compliance requirements. Ensure that your automation solutions adhere to all relevant security standards and regulations.
Automation in IT Service Management (ITSM) is continuously evolving and is shaped by several current trends. These trends include the increased use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), the integration of cloud technologies, and a focus on end-to-end automation.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are changing the way IT services are delivered. By leveraging these technologies, IT organizations can make precise predictions, perform proactive error correction, and offer personalized user experiences. These developments enable the automation of increasingly complex tasks and further improve efficiency.
Cloud Technologies
The integration of cloud technologies into ITSM automation provides flexibility and scalability. Companies can dynamically adjust their IT services and quickly respond to changes in the business environment.
End-to-End Automation
Another important trend is end-to-end automation, which encompasses all phases of the IT service lifecycle. This means that not only individual processes but entire workflows are automated to ensure seamless and efficient service delivery.
Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation combines traditional automation with advanced technologies like AI, ML, and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). This integration enables IT organizations to automate even more complex and cognitively demanding tasks, leading to higher efficiency and better decision-making.
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation takes it a step further than intelligent automation and aims to automate every possible IT process. This includes the identification, analysis, design, automation, and monitoring of all IT processes. Hyperautomation enables companies to continuously optimize their IT services and quickly respond to new requirements.
The increasing process automation has far-reaching implications for IT organizations. The development requires an adaptation of organizational structures and processes, as well as continuous training of employees.
With advancing process automation, new roles and skills are needed. IT professionals must further develop themselves in areas such as data analysis, AI, and ML to effectively utilize the new technologies. At the same time, roles like automation specialists and process designers will gain significance.
The ability of IT departments to effectively use process automation will become a decisive competitive factor for the entire organization. Organizations that successfully implement process automation can increase their efficiency, reduce costs, and offer higher service quality. They thereby realize crucial advantages over their competitors and drive their own growth.
OTOBO | Simplify work and create exceptional service experiences.
The Source Code Owner and Maintainer of OTOBO.
Service Management Platform
OTOBO Demo
OTOBO Download
OTOBO Documentation
Report a security issues:
security@otobo.org

 OTOBO 11.0.4
OTOBO 11.0.4